5S system is one of the fundamental tools that build the Lean Management philosophy. Practice shows that most companies begin their adventure with lean manufacturing from the implementation of the 5S system. This is the correct approach, as this method is oriented towards the stabilization of processes, which is the foundation of the Toyota Production System. Unfortunately, the 5S system is very often associated by employees with just cleaning their workplace. If the 5S system ended with cleaning, we would only have 3 steps of this approach – cleaning is the 3.S. The 5S system primarily aims to improve and maintain the quality of the workplace. One of the guiding principles of the 5S system is: “Everything has its place and everything is in its place.” You can learn about the 5S System during practical workshops.
Table of Contents
ToggleProcedure for Implementing the 5S System
Table 1 shows the procedure for implementing the 5S system at any workplace. This diagram was developed on a Job Breakdown Sheet used in the Training Within Industry – TWI program.
Table 1. Scheme of the procedure for implementing the 5S system
| Important steps | Key points | Reasons for key points |
| What should be done | How it should be done | Why should you do it this way |
| 1. Sorting | 1. Separating what is needed from what is not needed: -tools -instructions, -materials, -Etc. |
1. Maintaining order in the workstation is easier when you only have at work what you need daily. |
| 2. Discarding any unnecessary parts or marking them with a red label | 2. If you are not sure whether to discard a given part, leave it in the red label area and return to it after a certain amount of time (e.g. a month). You can then take action. Throw away any unnecessary things. | |
| 2. Systematics | 1. Marking places for parts and tools that you need on workstations | 1. You will always know what you are missing on the workstation. It will also be easier to keep order. |
| 2. Using colors (visual control) | 2. Colors are an essential part of visual control. People absorb as much as 83% of information through sight. Try to use colors wherever possible. | |
| 3. Defining limits, levels, and directions. | 3. This will help you keep the required number of materials and tools on the workstation. This will facilitate self-discipline in following the rules. | |
| 3. Cleaning | 1. When cleaning, look for faults and problems in your workstation | 1. Cleaning is checking. You do not clean just to keep the machine or workstation tidy. The main purpose of cleaning should be to identify irregularities. |
| 2. Setting up a cleaning schedule | 2. Thanks to the schedule, you will be able to effectively audit the 5S system maintenance process in the company. | |
| 4. Standardization | 1. Establishing standards for cleaning and arranging tools and materials on the workstation. | 1. The workstation should be organized in such a way that everyone knows how to find themselves on it – not only you. The written standard will help with this. |
| 2. Establishing a schedule of audits | 2. To maintain the system. Only supervisions and audits are a guarantee that 5S activities will become a habit for employees. | |
| 5.
Self-discipline |
1. Carrying out the tasks that result from audits. | 1. An audit is not control. This is an opportunity for improvement. Expect audits at your workstation. If any recommendations come from them, follow them. Self-discipline is about following the rules every day. Don’t be afraid of audits. Treat them as an opportunity to test your conduct. |
Example of 5S System Implementation
6S – Safety as the First or the Sixth “S”
How to Implement Safety?
- Important steps (what are we doing?)
- Key points (how do we do it?)
- The reasons for the key points (why do we do it the way we do it?)
- Words that tell you to work safely
- Orders to use personal protective equipment
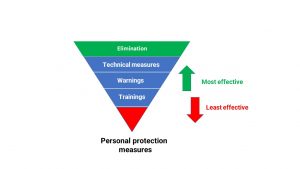
(Fig. 1). Hierarchy of control
TWI Job Safety
- Step – Identification of the places that are the causes of hazards
- Step – Identification of remedial measures
- Step – Implementation of remedial actions.
- Step – Controlling the results
TWI Job Breakdown for 6.S – Safety
Table 2. Scheme of proceeding in the case of O.S – occupational safety
| Important steps | Key points | Reasons for key points |
| What should be done | How it should be done | Why should you do it this way |
| 1. Creation of a safe workplace | 1. Identifying places that are threats | 1. To determine where an accident could occur in the future. Use the hazard identification worksheet as inspiration. |
| 2.Defining countermeasures for threats | 2. To cover all the hazards that could lead to an accident. | |
| 3.Implementing countermeasures | 3. These measures will, in practice, protect employees. Remember to start with the elimination of threats, and then if it is impossible, implement technical measures. Treat personal protective equipment as the least effective measure. | |
| 4. Training employees about the hazards occurring on workstations | 4. So they become aware of possible dangers at a workstation before they start implementing the 5S system. | |
| 5. Controlling results | 5. To check that countermeasures are in place and that no additional hazards have arisen. |
Summary: 5S system or the 6S system
The exploration of the 5S system within the context of Lean Management reveals its crucial role in enhancing workplace organization and efficiency. Its common misinterpretation as merely a cleaning protocol underscores the need for a deeper understanding and implementation of its comprehensive principles, which include sorting, systematics, cleaning, standardization, and self-discipline.
The proposed evolution to the 6S system, with the integration of Safety as a foundational element, signifies a paradigm shift in how safety is perceived and implemented in workplace organizations. This approach challenges the conventional relegation of safety to a mere adherence to protective measures and advocates for its prioritization as the initial step in the process.
In conclusion, the effective implementation of the 5S or 6S system transcends mere cleanliness and organization. It embodies a holistic strategy that intertwines efficiency, safety, and continuous improvement, crucial for fostering a productive, safe, and disciplined working environment. By redefining safety as a proactive and foundational element, the 6S system offers a more robust and comprehensive framework for workplace optimization, ensuring that safety and efficiency are not mutually exclusive but rather integral and complementary aspects of the same continuum.

Dr. Bartosz Misiurek is a co-founder of a few start-ups like Leantrix, Lean Community, Leancoin, etwi, Lean Global Consulting, Sallar. He is a CEO at LeanTrix Ltd., Leancoin Ltd, Do Lean IT OU, and a Member of the Board at Astral Hodling OU. Author of the book “Standardized Work with TWI: Eliminating Human Errors in Production and Service Processes.” He works as Sr Manager and TWI Global Coach at Automotive Company.